Sintered ferrite is an important magnetic material made from strontium oxide, barium oxide, and iron oxide as raw materials, and manufactured through ceramic processes (pre firing, crushing, powder milling, compression molding, sintering, and grinding). It is widely used in fields such as electronics, automobiles, and energy. The following are the top 5 major application markets worldwide (based on industry data statistics in recent years).
Top 5 Uses and Proportion of Sintered Ferrite Magnets
1. Motor and automotive fields (approximately 35%-40%). Mainly used in automotive motors (such as windshield wiper motors, seat adjustment motors, starter motors), electric window motors, fuel pump motors, etc., as well as auxiliary motors for new energy vehicles (such as cooling fans, water pumps), etc.
Common shapes of sintered ferrite in electric motors - arc shape
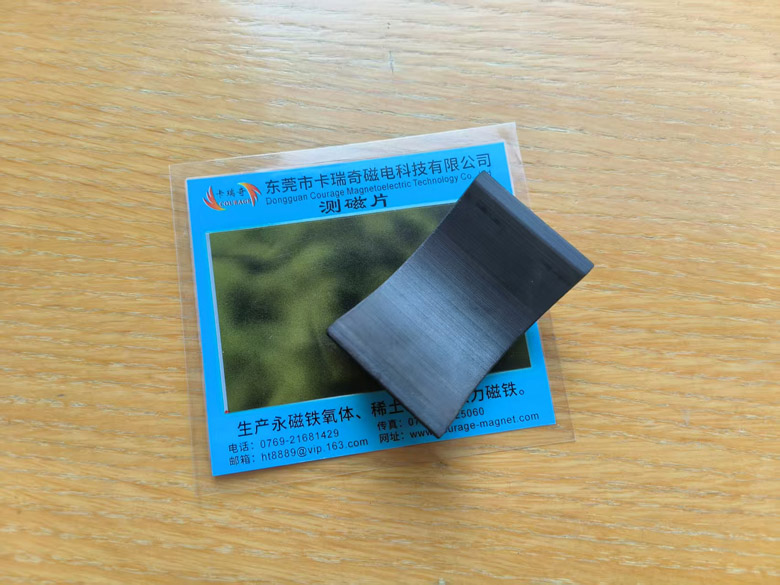

2. Home appliances (approximately 25%-30%), mainly used in refrigerator compressors, air conditioner fan motors, washing machine motors, water pumps, etc. Its low cost and high stability make it the material of choice for home appliance motors.
3. Consumer electronics (approximately 15%-20%), such as audio and multimedia equipment, portable fans, and mid- to low-end consumer electronics, account for a high proportion.
4. Industrial equipment (approximately 10%-15%). Sintered ferrite magnets are used in some low-end or specific types of power tools, such as electric pruning shears, electric lawn mowers, angle grinders, simple electric grinders, and electric knife sharpeners.
5. Other areas (approximately 5%–10%). These include niche applications such as toys, packaging, office supplies, magnetic separation equipment, and door magnets.
The above is an introduction to the top 5 applications and proportions of sintered ferrite magnets. Our company can process various ordinary and special ferrite permanent magnets. Customers who need to purchase are welcome to provide drawings or specifications for inquiry.
More knowledge about sintered ferrites;
Ferrite permanent magnets material composition detail
Do I have to open a mold for sintered ferrite?
Main differences between injection molded magnets and sintered magnets
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier