Cube magnet is a common type of magnet shape, with equal length, width, and height dimensions. It is widely used in various microelectronic products and precision instruments. With advancements in technology, magnets are becoming increasingly smaller and more refined. So, how small can a cube magnet actually be?
The minimum size of a cube magnet is limited by the characteristics of the material itself, processing accuracy, and usage requirements. Taking neodymium iron boron (NdFeB) and ferrite as examples, there are some differences in their minimum size.
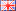
Accompanying image shows a rare earth neodymium cube magnet.
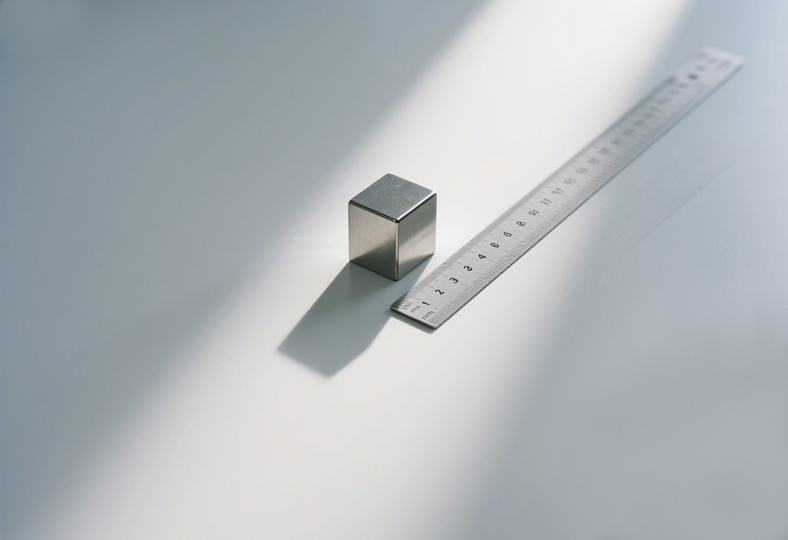
Cube magnets made of neodymium material can achieve very small sizes, but due to their high brittleness and processing difficulty, their minimum size is usually around 0.5 mm to 1 mm. Smaller sizes can be manufactured through advanced precision machining processes, but in practical applications, such small-sized magnets may face problems such as weak magnetic force and fragility.
Although ferrite materials have high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, their magnetism is much weaker than neodymium iron boron materials, so their minimum size is usually slightly larger, generally above 2mm.
As for samarium cobalt material, the smallest cube magnet size that can be processed is similar to that of neodymium magnets, and it is generally replaced by neodymium material.
The above is an introduction to how small cube magnets can be processed. If you need a quote for micro cube magnets or would like to request a sample, please feel free to send us an email or leave a message online.
Related cube permanent magnet cases;
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier