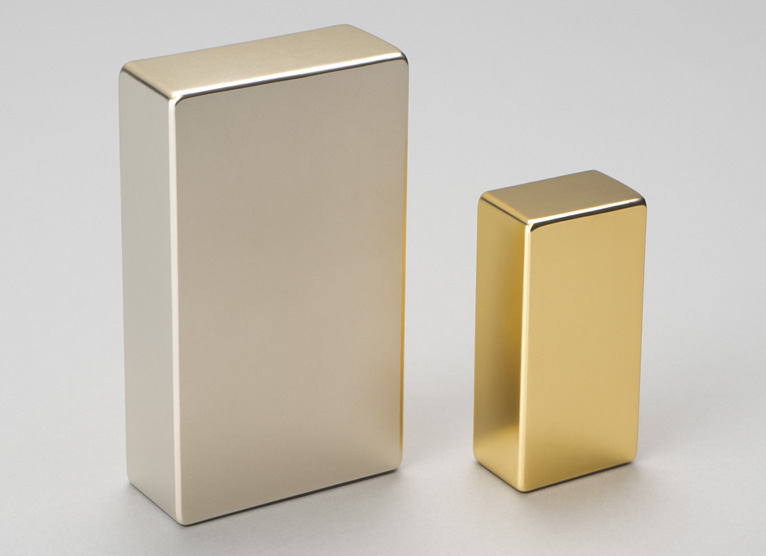
Rectangular rare earth magnets are powerful permanent magnets shaped like rectangles, typically made from neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) material, making them one of the strongest permanent magnets available today. They can also be made from samarium-cobalt (SmCo) material, which is more heat-resistant than neodymium material. Below are the top 10 frequently asked questions about rectangular rare earth magnets, along with their answers, compiled by xiao fu.
Rectangular rare earth neodymium magnets, which can be coated and sized according to customer requirements.

1. How can the magnetization direction of rectangular rare earth magnets be selected?
There are three main options: magnetization along the length, magnetization along the width, and magnetization along the thickness.
2. What are the applications of rectangular rare earth magnets?
This type of magnet is widely used in electric motors, sensors, electric vehicles, mechanical equipment, medical devices, and various consumer electronics.
3. Are rectangular rare earth magnets prone to breaking?
Due to the high hardness and brittleness of neodymium iron boron magnets, impact or excessive bending may cause them to break or shatter, especially thinner ones.
4. How to determine the optimal length-to-width ratio for rectangular rare earth magnets?
When the length-to-width ratio is close to 1:1, the magnetic field distribution is most uniform. Slender types (length-to-width ratio > 2:1) have a more concentrated magnetic field at the ends. It is generally recommended to control the length-to-width ratio between 1:1 and 3:1 to balance performance and cost.
5. How can rectangular rare earth magnets be prevented from cracking?
A reasonable length-to-width-to-thickness ratio should be maintained to avoid overly elongated or thin designs. Chamfering of 0.1–0.3 mm should be performed at the corners, and hammering or forced assembly should be avoided during installation.
6. How to choose the surface treatment for rectangular rare earth magnets?
For neodymium materials, zinc plating can be selected for low cost. For certain requirements on appearance and corrosion resistance, nickel plating can be selected. For more severe environments, epoxy and parilin are recommended. Samarium cobalt materials do not require surface treatment.
7. How high a temperature can rectangular rare earth magnets withstand?
Ordinary neodymium-iron-boron magnets can generally operate stably within a temperature range of 80°C. For higher heat resistance, grades such as H, SH, and UH can be selected. Ordinary samarium-cobalt magnets can withstand temperatures of 250-350°C.
8. How thin and how small can rectangular rare earth magnets be made?
The thickness of both neodymium rectangular magnets and samarium-cobalt rectangular magnets can be processed to approximately 0.4 mm. The length can be processed to approximately 1.5 mm.
9. What types of rectangular rare earth magnets can be processed?
Customers often choose to process countersunk holes, through holes, slots, bevels, etc.
10. What are the tolerances for rare earth rectangular magnets?
Generally ±0.05 mm, but can also be controlled to ±0.03 mm or +0.02 mm, -0.02 mm.
The above are some common questions about rare earth rectangular magnets. We welcome you to consult us or customize rare earth rectangular magnets. Whether they are small, thin, flat, or large, we can process them according to your requirements.
The following article compares the two.
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier