Previously, we've covered comparisons between various magnet types, such as ceramic magnets vs. rare earth magnets, ceramic vs. samarium cobalt, neodymium vs. samarium cobalt, sintered vs. bonded, and so on. Today, we'll explore the differences between injection-molded magnets and rubber magnets.
Differences in Material Composition and Production Processes
Injection-molded magnets are typically manufactured by blending magnetic powders (such as neodymium or ferrite) with plastics (like nylon, polyester, or ABS) through an injection molding process. Their high magnetic powder content yields superior magnetic properties.
Rubber magnets are primarily composed of a rubber base material (e.g., EPDM, TPR) blended with magnetic material (e.g., ferrite powder), typically exhibiting weaker magnetic properties. They offer high flexibility and are suitable for applications requiring deformation or bending.
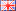
Illustration: 8-pole injection-molded ferrite ring, 25x8x5mm
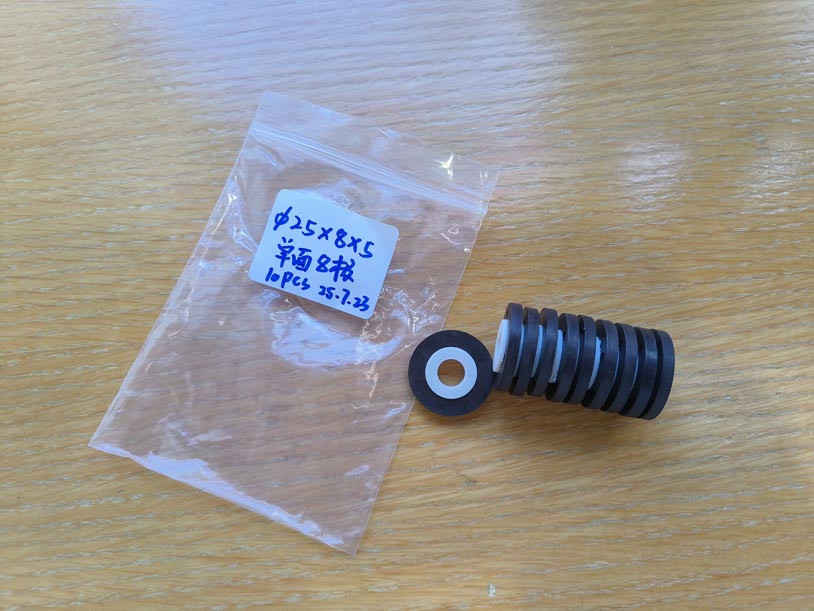

Magnetic Strength Differences
Injection-molded magnets exhibit stronger magnetic properties due to their higher magnetic powder content (typically 50%-80%), with neodymium iron boron injection-molded magnets achieving magnetic energy products of 8-12 MGOe. In contrast, rubber magnets contain lower magnetic powder ratios (usually 20%-50%), resulting in magnetic energy products typically ranging from 1-5 MGOe and relatively weaker magnetic properties.
Flexibility and Machinability Comparison
Although injection-molded magnets possess a certain degree of hardness, they still exhibit good formability and can be manufactured into various complex shapes. However, they are not as flexible as rubber magnets.
Rubber magnets offer excellent flexibility and elasticity, capable of bending, stretching, and shearing. They are suitable for applications requiring a certain degree of deformation.
Application Scenario Differences
Injection-molded magnets are primarily used in motors, magnetic sensors, encoders, and electrical appliances. Rubber magnets, on the other hand, are predominantly used in low-load applications such as advertising display boards, refrigerator magnets, and vehicle decals.
Price Comparison
Injection-molded magnets command a higher price primarily due to their higher proportion of magnetic materials and more complex manufacturing processes. Rubber magnets are relatively less expensive, mainly because they utilize cheaper base materials with a lower magnetic powder content and simpler production techniques.
The above compares these two types of magnets, which differ in appearance, applications, magnetic properties, price, and other aspects.
You might want to know:
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier