In modern motor systems, position and rotational speed detection are critical factors for control precision and operational efficiency. As a common magnetoelectric sensing component, Hall sensors require specific magnetic parts to achieve accurate sensing. Among these, the motor Hall sensor magnetic ring serves as one of the core components.
Motor Hall Sensor Magnetic Ring, typically mounted on the rotor shaft or end position of an electric motor, features a ring-shaped structure. Its function is to provide regularly distributed magnetic poles. As the motor rotates, the Hall element passing through the magnetic ring senses changes in the magnetic field, thereby generating electrical signals. These signals are captured by the control chip, enabling the calculation of the rotor's position, rotational speed, and direction of rotation. This facilitates brushless motor control (such as BLDC and PMSM) and precise commutation.
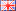
The attached image shows the 12 poles magnetic ring of the motor Hall sensor
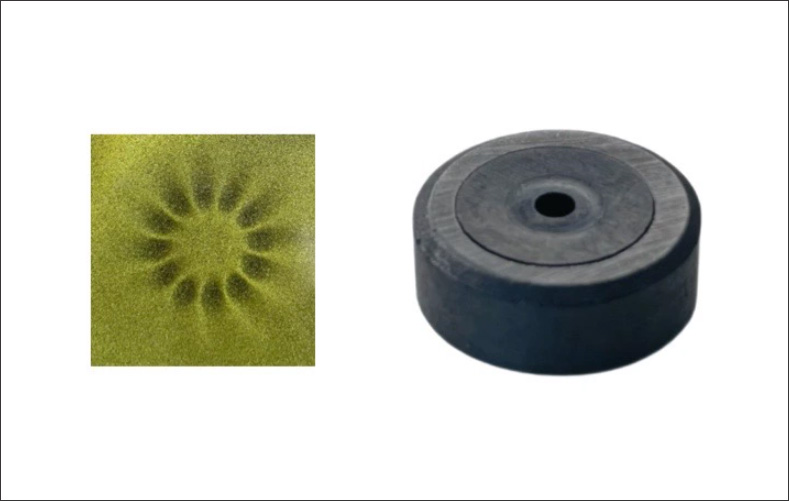

During the manufacturing process, the magnetic ring will form a multipole magnetization through a magnetizing fixture, where N and S poles are alternately arranged on the annular magnet. For example, common magnetic rings with 4-pole, 8-pole, 12 pole, 22 pole, 24 pole, or even higher pole numbers. When the motor rotates, the magnetic field detected by the Hall sensor will show regular changes, forming pulse signals that are ultimately converted into position information.
In terms of magnetic ring materials, different materials directly affect signal stability and cost. Commonly used ones include sintered and injection molded ferrites, bonded or injection molded neodymium magnets. Sintered or injection molded ferrite has low cost, good high temperature resistance, and high stability. The disadvantage is that the magnetic energy product is low, and the volume often needs to be slightly larger. Neodymium material has strong magnetic properties and can provide strong magnetic fields in small volumes with clear signals, but the cost is also much higher. It is mostly used in high-end motors, such as precision servo motors and robot motors.
For installation, the center of the magnetic ring must align precisely with the motor shaft. If the magnetic ring is off-center or tilted, it will cause unstable Hall sensor output, affecting motor operation. After installation, connect an oscilloscope and slowly rotate the motor to confirm the waveform is perfect.
The above covers the common materials used for magnetic rings in motor Hall sensors. If you are seeking samples, please provide drawings or specific requirements such as magnetic ring dimensions, pole count, and surface flux density.
Recommended related magnetic rings;
Single-sided 6-pole plastic ferrite magnet ring 9.5x2x2mm
Inner hole 2mm radial 24 pole ceramic magnetic ring 14x2x5.5mm
22 pole radial injection molded neodymium magnet ring Φ14mm
Some people are still asking;
Which side of the magnet should be induced by the Hall sensor?
Relation Between Hall and Pole Pair Number of Brushless Motor
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier