When engineers are designing motors, the selection and optimization of magnets is a key factor in performance, efficiency and reliability. The following are the relevant aspects of magnets that need to be considered, and we hope that you will find them helpful.
1. Aspects of magnetic performance parameters
The remanent magnetism (BR) indicates the flux density retained by the magnet after magnetization, which determines the air gap magnetic field strength and directly affects the motor output torque and power density. The endowed coercivity indicates the magnet's ability to resist demagnetization, which is especially important under high temperature and high load conditions. Maximum magnetic energy product ((BH)max) indicates the maximum magnetic energy that can be provided per unit volume, which is related to the power density of the motor. The linearity of the shape of the demagnetization curve affects the stability of the magnetic field, and irreversible demagnetization needs to be avoided during load or temperature changes.
2, Type of material
Too much has been introduced in this website. NdFeB has high magnetic energy area, suitable for high performance motors, temperature stability needs to be considered. Ferrite is low cost and high temperature resistant (>250°C), but has a low magnetic energy product, suitable for low cost or high temperature environments. Samarium Cobalt is high temperature resistant (>300°C), corrosion resistant, but high cost, suitable for aerospace, military or special industry. As for Alnico is hardly used in motors nowadays.
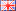
The attached image shows a 6-pole ring magnet for the motor

3. Temperature resistance aspect
Ensure that the magnet does not experience irreversible demagnetization at the operating temperature of the motor. The temperature coefficients of remanence (Br) and coercivity (Hc) need to match the operating temperature range of the motor. For example, the Br temperature coefficient of neodymium iron boron is about -0.12%/° C, and compensation design is required at high temperatures.
Learn more: List of high temperature resistance permanent magnets
4. Size and shape aspects
The shape design of the magnet (e.g. rectangle, arc/rectangle/fan/wedge, ring, hollow cylinder) has to match the structure of the stator/rotor. The tolerance of the magnet should be well controlled, which has an important effect on the assembly accuracy and air gap size.
5. Magnetization aspect
Mainly radial and radial multipole magnetization are used, but axial or axial multipole magnetization can also be used, which needs to be matched with the type of motor.
The above is about the design of the motor for the magnet needs to be considered in the introduction, such as your company needs to be used in the motor on the magnet welcome to contact us to provide samples, quotations.
Related Article Recommendations;
Application of Ndfeb neodymium magnet in stepper motor
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier