In the rapid advancement of robotics, neodymium iron boron (NdFeB) permanent magnets have emerged as core materials for drive systems, sensing applications, and specialized uses due to their exceptionally high magnetic energy product and compact size. Below are the application details.
First are the motors and drive systems. These primarily include joint drives, mobile platform drives, and micro-actuators.
Industrial robots and collaborative robots (such as UR and ABB YuMi) widely adopt neodymium iron boron permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) for their joint modules. These motors deliver high torque density and rapid dynamic response, meeting the demands for high-precision motion.
Hub motors for AGVs and leg drive motors for quadrupedal robots (e.g., Boston Dynamics Spot) rely on neodymium iron boron for efficient energy conversion, balancing lightweight design with extended endurance.
Surgical robots (e.g., the Da Vinci system) utilize miniature motors leveraging neodymium iron boron's miniaturization advantages to achieve ultra-precise operational control.
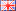
Illustration shows a magnetic code disc for absolute encoders used in robots.

Next are applications in sensors and feedback systems. For instance, robotic joints are often equipped with multi-turn magnetic encoders, utilizing neodymium iron boron magnetic rings as core components to enhance angular measurement precision while offering superior anti-interference capabilities. Hall effect sensors employ neodymium iron boron as excitation magnets to detect motor rotor positions in real time, thereby optimizing closed-loop control and improving overall motion stability.
For the dexterous fingers and joint motors of humanoid robots (such as Tesla Optimus), high-power-density micro drivers are required. Neodymium-iron-boron provides support for the flexibility of human-like movements. In scenarios with extremely high demands for lightweight and high thrust (such as the brushless motors of DJI drones), neodymium-iron-boron magnets significantly improve the thrust-to-weight ratio and play a crucial role in the propulsion motors of underwater robots.
Typical Application Cases
Industrial Robotic Arms: Six-axis robotic joint motors utilize annular magnet arrays to achieve ±0.02mm repeatability positioning accuracy;
Humanoid Robots: Hollow-cup motors employ ultra-thin neodymium magnets (0.4mm thickness) to meet the flexible driving force requirements for finger joints.
In summary, neodymium iron boron magnets play a pivotal role in multiple core functions within robotics, including motor drives, sensing and detection, end-effectors, and structural connections. They serve as the key magnetic material enabling robots to achieve high performance and intelligent operation.
Selection of relevant neodymium magnets;
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier