As we all know, bonded neodymium iron boron magnets are widely used in motors, electrical appliances, and other products due to their unique properties. Having worked with magnets for over a year, I have been asked by many customers, “How thin can you make the single-sided wall thickness of your bonded neodymium magnets?”
Before introducing this issue, let's first introduce what is the "single-sided wall thickness" of a magnet?
"Single-sided wall thickness" refers to the difference between the outer diameter and inner diameter of a ring-shaped magnet divided by two, i.e.: Single-sided wall thickness = (Outer diameter - Inner diameter) ÷ 2
For example, if a ring-shaped magnet has an outer diameter of Φ18mm and an inner diameter of Φ16mm, the single-sided wall thickness is (18-16)/2 = 1mm.
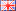
The image shows a bonded neodymium ring magnet with a wall thickness of approximately 1 mm.

Regarding the minimum single-sided wall thickness that can be achieved for bonded neodymium-iron-boron magnets, many people might say around 1mm, as most bonded magnetic rings typically have a single-sided wall thickness of around 1mm. In fact, bonded neodymium iron boron magnets can be made even thinner—0.6mm and 0.5mm are both feasible, depending on your specific requirements. [One of our clients in the medical device industry, for example, uses a single-sided wall thickness of 0.5mm, with overall dimensions that are also relatively small.]
Note: Thin-walled structures are not suitable for high coercivity sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnets, as they tend to be brittle. Bonded magnetic rings with thin walls have slightly lower magnetic performance but better uniformity. Thin-walled + high-uniformity bonded ring structures can be used for rotor outer sleeves.
Related thin-walled magnets;
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier