In the field of magnetism, the direction and distribution of magnetic fields play a crucial role in their application effectiveness. In addition to the well-known axial magnetic fields, another equally important but often overlooked form of magnetic field—radial magnetic fields—also plays a key role in various fields such as motors, sensors, and precision instruments.
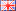
Radial magnetic field distribution of a ring magnet

The formation of a radial magnetic field typically relies on magnets of specific shapes, particularly circular, ring shaped, or spherical magnets. Taking a circular magnet as an example, when it is magnetized, magnetic field lines radiate outward from the center of the magnet, forming a radial magnetic field. Unlike traditional axial magnetic fields, radial magnetic fields exhibit a uniform, radial distribution in space, making them suitable for applications requiring a uniform magnetic field distribution.
In a radial magnetic field, the strength of the magnetic force is inversely proportional to the distance from the center of the magnet. That is, the farther from the center of the magnet, the weaker the magnetic field strength. This distribution characteristic gives radial magnetic fields unique advantages in certain specific applications.
Typical Applications of Radial Magnetic Fields 1 - Motor
In permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM), radial magnetic fields help achieve stable motor operation. Especially in small motors, the design of radial magnetic fields helps improve efficiency and reduce size. In addition, generators often rely on radial magnetic fields to efficiently generate current.
Typical Applications of Radial Magnetic Fields 2 - Magnetic Sensors
Radial magnetic fields are also widely used in magnetic sensors, especially when measuring the interaction between objects and magnetic fields. Radial magnetic fields provide a uniform magnetic field environment, enabling sensors to respond more sensitively and stably.
The radial magnetic field of magnets also facilitates multipole magnetization designs (such as 4-pole, 8-pole, 10-pole, etc.), which helps meet complex application requirements, especially in compact, high-speed motor designs where it offers unique advantages.
The above is an introduction to radial magnetic fields, which enable magnets to radiate stronger vitality in efficient, precise, and compact modern technological applications.
Introduction to related radial magnets;
Radial Ring Magnets [Meaning Uses Magnetization Diagram]
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier