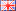
The stator and rotor are two key components in an electric motor. They work together to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. The following is a detailed explanation of the stator and rotor of an electric motor and their respective functions.
The stator is the stationary part of an electric motor, fixed to the housing. It mainly consists of a core and windings. The core is made of laminated silicon steel sheets to reduce eddy current losses. The windings generate a rotating magnetic field (in AC motors) or a fixed magnetic field (in DC motors) when energized.
The rotor is the rotating part of an electric motor, located inside the motor. It consists of an iron core (also made of laminated silicon steel sheets) and conductive materials (such as copper or aluminum windings, permanent magnets). Types of rotors include squirrel-cage (asynchronous motors), wound (powered by slip rings), and permanent magnet (such as electric vehicle motors).
Electric motor rotor and stator structure
The primary function of the stator is to generate the magnetic field that drives the rotor's motion. In an electric motor, the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator windings when energized attracts the rotor to rotate, thereby converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Other functions: In a generator, the stator also serves as a conductor. When the rotor rotates, it cuts through the magnetic field lines, inducing a current in the stator windings, thereby converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. However, this function is not present in an electric motor.
The main function of the rotor is to rotate under the action of a magnetic field and output mechanical energy. The rotor interacts with the magnetic field generated by the stator through the principle of electromagnetic induction, generating torque and driving the load to rotate.
Specific process: In an AC asynchronous motor, the rotor current is induced by the stator magnetic field (without the need for an external power source), and thus rotates under the action of the magnetic field. In permanent magnet motors, the rotor directly generates a magnetic field from the permanent magnet and interacts with the stator magnetic field to achieve rotation.
In summary, the stator and rotor of an electric motor have distinct structural and functional characteristics and work together. The stator, as the stationary part, establishes a magnetic field, while the rotor, as the rotating component, converts electromagnetic energy into mechanical motion. The two interact through magnetic fields to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, thereby driving the load to rotate.
Related motor magnet columns;
DC Motor Rotor & Stator Magnets [Samples Supplier Custom]
Other questions
Is the rotor of a permanent magnet motor a permanent magnet?
Motor arc rotor magnets is too strong how to assemble more safe
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier