In modern industrial applications, neodymium magnets are widely used due to their excellent magnetic properties. However, one obvious drawback of ordinary neodymium magnets is their poor high-temperature performance, their magnetic properties deteriorate significantly at temperatures above 80°C, and they may even become demagnetized. To address this issue, “high-temperature neodymium magnets” have emerged as the ideal magnetic material for many high-temperature environments. So, what are high-temperature neodymium magnets? How do they differ from ordinary neodymium magnets? What temperatures can they withstand, and in which typical fields are they applicable? These questions will be addressed in detail below.
What are high temperature neodymium magnets?
High-temperature neodymium magnets refer to special materials that maintain magnetic stability in high-temperature environments through formula adjustments (such as adding elements like cobalt, dysprosium, and terbium).
Applications of high-temperature neodymium magnets in the motor industry
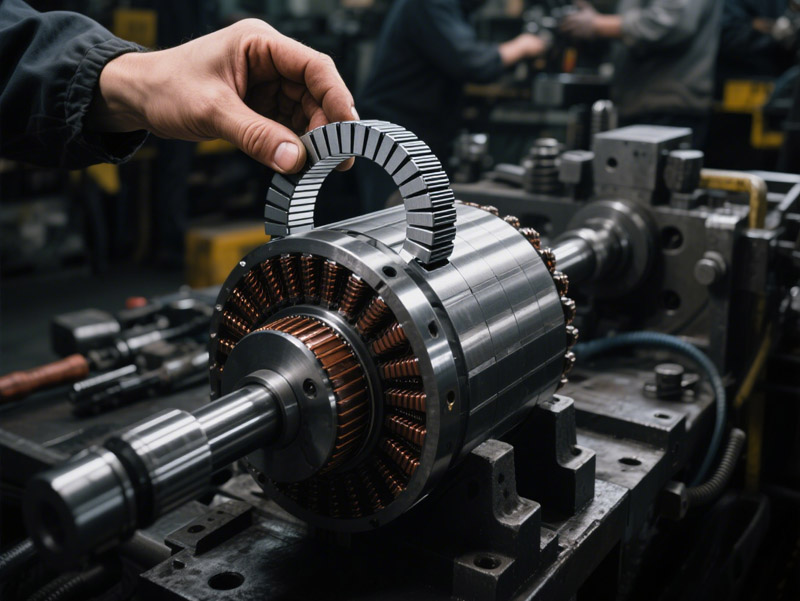

Difference between high-temperature neodymium magnets and ordinary neodymium magnets
Standard neodymium magnets (N35) typically have a maximum temperature rating of 80°C. High-temperature neodymium magnets, however, offer a broader operating temperature range. For instance, H-grade neodymium magnets can maintain stable performance at temperatures up to 120°C, while EH-grade magnets can withstand temperatures exceeding 200°C.
Ordinary neodymium magnets contain few elements and are low in cost, while high-temperature neodymium magnets contain rare earth elements such as cobalt and dysprosium, which are more expensive.
In terms of application scenarios, high-temperature neodymium magnets are mostly used in high-temperature motors, automotive motors, industrial fans, compressors, high-temperature sensors, vacuum pumps, high-temperature braking systems, etc. Ordinary neodymium magnets are mostly used in various fields with low temperature requirements, such as electronic equipment, digital products, toys, magnetic adsorption devices, etc.
Will high-temperature magnets demagnetize when exposed to high temperatures?
Ordinary neodymium-iron-boron magnets will, but high-temperature neodymium magnets will not. They can maintain their magnetic properties within a specified temperature range and are more stable in long-term use.
What grades of high-temperature neodymium magnets can you provide?
Common high-temperature grades include: N35SH, N38SH, N42SH, N35UH, N38UH, N35EH, etc. For more details, please refer to the neodymium magnet grade chart.
Is the magnetic force of high temperature neodymium magnets weaker than that of ordinary magnets?
For the same volume, high-temperature magnets are slightly weaker, but still much stronger than high-temperature magnets such as samarium cobalt or aluminum nickel cobalt. If there are magnetic force requirements, we can increase the volume of the magnet to compensate.
Can it replace samarium cobalt magnets?
In certain medium - and high temperature applications (such as below 150°C), high-temperature neodymium magnets can replace samarium cobalt magnets, offering stronger magnetic performance and lower prices. However, at extremely high temperatures (above 200°C), samarium cobalt magnets remain more reliable.
The above is an introduction to high-temperature neodymium magnets. If your company needs to purchase this type of magnet, please feel free to provide relevant data or drawings.
Supplementary introduction article;
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier